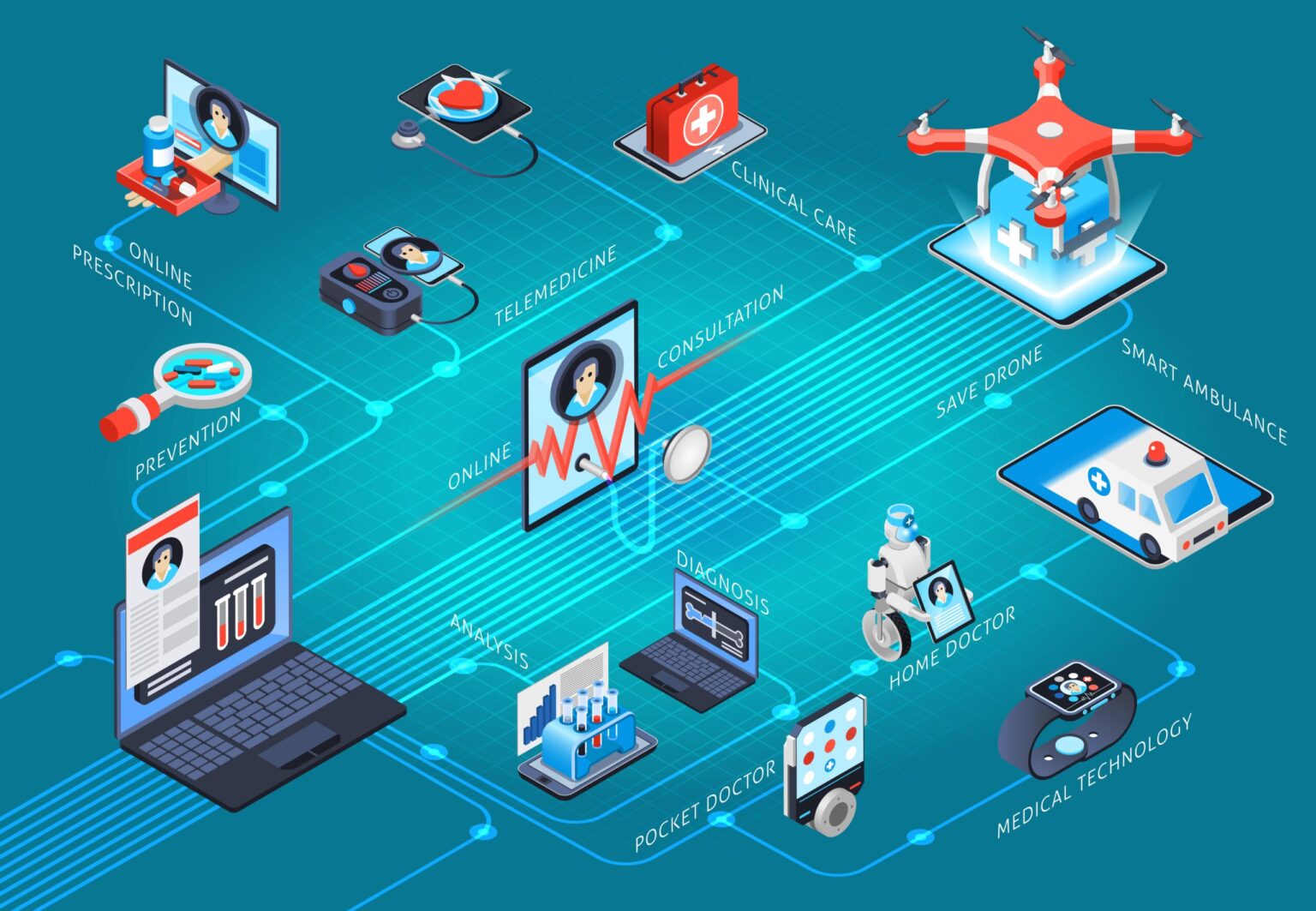
The future of telemedicine holds great potential to transform healthcare delivery and improve access to medical services. Telemedicine, also known as telehealth, refers to the use of technology to provide remote healthcare services, consultations, and monitoring. Here are some key aspects that highlight the transformative impact of telemedicine:
- Increased Access to Healthcare: Telemedicine overcomes geographical barriers and improves access to healthcare, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas. It allows patients to connect with healthcare professionals through video consultations, eliminating the need for travel and reducing waiting times. This is particularly beneficial for patients with limited mobility, chronic conditions, or limited access to healthcare facilities.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Telemedicine enables remote patient monitoring through the use of wearable devices, connected medical devices, and health apps. Patients can track their vital signs, symptoms, and medication adherence, which can be transmitted to healthcare providers in real time. This allows for proactive management of chronic conditions, early detection of health issues, and timely interventions, reducing hospital admissions and improving patient outcomes.
- Continuity of Care: Telemedicine facilitates continuity of care by enabling seamless communication and collaboration between healthcare providers. Electronic health records and telemedicine platforms ensure that patient information is easily accessible, allowing providers to make informed decisions and coordinate care effectively. This is particularly valuable for patients with complex medical conditions who require multiple specialists’ input and care coordination.
- Specialist Consultations and Second Opinions: Telemedicine allows patients to access specialist consultations and second opinions without the need for referrals or extensive travel. Through video consultations, patients can connect with experts across various medical fields, regardless of their geographical location. This not only saves time and travel expenses but also ensures that patients receive specialized care and appropriate treatment plans.
- Home Healthcare and Remote Services: Telemedicine enables the delivery of home healthcare services, reducing the need for hospital visits for certain conditions. Patients can receive post-operative follow-ups, chronic disease management, and rehabilitation services from the comfort of their homes. Remote services, such as telepharmacy and teletriage, allow healthcare professionals to assess and address patients’ needs remotely, ensuring timely care and reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
- Telepsychiatry and Mental Health Services: Telemedicine plays a crucial role in expanding access to mental health services. Telepsychiatry allows patients to connect with mental health professionals for consultations, therapy sessions, and medication management. It reduces stigma, increases convenience, and improves access to mental healthcare for individuals in underserved areas or those unable to seek in-person services.
- AI and Telemedicine Integration: Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are increasingly being integrated into telemedicine platforms, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, detect patterns, and assist healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can also provide triage services, answer basic medical questions, and provide personalized health recommendations.
The future of telemedicine lies in further advancements in technology, connectivity, and regulatory frameworks. It holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery by increasing access to care, improving patient outcomes, and reducing healthcare costs. However, challenges related to privacy, security, reimbursement policies, and equitable access to technology need to be addressed to ensure the widespread adoption and success of telemedicine in the future.