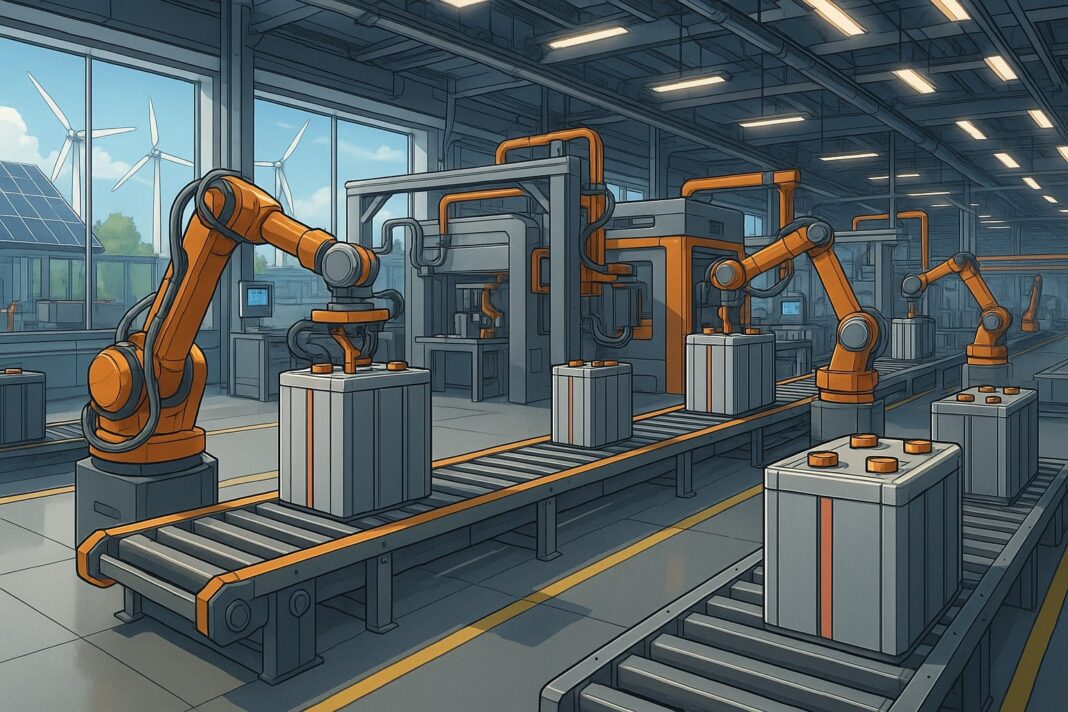
The global race for electric mobility has turned battery factories into some of the most advanced industrial facilities ever built. By 2030, next-generation battery plants—also known as Gigafactories—will look less like factories and more like AI-driven clean energy labs, powered by automation, robotics, and sustainable systems.
With demand for EV batteries expected to triple in the next five years, future battery factories are being designed to deliver precision, speed, safety, and zero carbon emissions.
1. Hyper-Automated Assembly Lines: Humans Supervise, Robots Execute
The battery plants of tomorrow are built around full automation, where robots conduct the most critical and hazardous tasks.
Robots handle:
- Electrode coating
- Cell stacking & welding
- Precision electrolyte filling
- High-speed quality checks
- Thermal performance testing
- Pack assembly
These tasks require micrometer accuracy and chemical safety that only advanced robotics can ensure.
Benefits of automation:
✓ Zero contamination
✓ Higher consistency
✓ Reduced defects
✓ Faster production cycles
✓ Lower labor risk
Human workers focus on monitoring, engineering, and overseeing robotic operations.
2. AI-Powered Quality Control: Every Cell Is Verified
Battery manufacturing demands perfection—one microscopic defect can lead to:
- Thermal runaway
- Reduced capacity
- Faster degradation
- Safety failures
Advanced AI systems continuously scan:
- Electrode alignment
- Weld patterns
- Impurity levels
- Internal resistance
- Cell pressure and gas formation
AI vision identifies defects 100x faster than traditional inspection.
3. Digital Twins: Virtual Factories Running in Parallel
The factory of the future is recreated as a digital twin—a virtual replica that runs simultaneously in the cloud.
It tracks:
- Production flow
- Material usage
- Energy consumption
- Machine health
- Predictive maintenance
With digital twins, manufacturers can simulate improvements without stopping real production.
4. Clean Energy Integration: Zero-Carbon Battery Plants
Tomorrow’s battery factories will be powered by:
-
Gigawatt-scale solar farms
-
Wind energy microgrids
-
Hydrogen fuel cells
-
Battery energy storage systems
Why clean energy matters:
Battery production is energy-intensive. Using renewables:
-
Cuts manufacturing emissions
-
Reduces operating costs
-
Makes EVs truly sustainable
Tesla, CATL, Hyundai, and Toyota already invest heavily in renewable-powered Gigafactories.
5. Closed-Loop Recycling: The Battery Goes Full Circle
Future plants won’t just build batteries—they’ll recycle them into new batteries.
Robotic recycling systems extract:
- Lithium
- Nickel
- Cobalt
- Copper
- Graphite
Recovered materials go right back into the production line.
This closed-loop system reduces waste and slashes raw material costs.
6. Autonomous Material Handling: No Human Touch Needed
AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) transport:
- Anode & cathode sheets
- Finished cells
- Dangerous chemicals
- Heavy battery packs
These systems optimize traffic inside the factory, preventing bottlenecks.
Smart inventory management ensures raw materials are always in the right place at the right time.
7. Safer Factories Through Robotics
Future battery plants elevate worker safety with:
- Isolated robotic welding zones
- Automated chemical handling
- Fire-proof cell testing chambers
- AI detection for electrical/thermal hazards
- Remote monitoring systems
Human workers are removed from high-risk environments.
8. The Battery Factory of 2035: What It Looks Like
Imagine walking into a future Gigafactory:
- Robotic arms assemble cells in cleanrooms
- AI supercomputers optimize production in real time
- Solar roofs power the entire plant
- Digital dashboards show live cell formation curves
- Recycling robots dismantle old batteries
It’s a self-learning, energy-neutral ecosystem producing millions of high-performance cells per year.
Conclusion
Battery factories are undergoing a profound transformation. Through automation, robotics, AI, clean energy, and recycling, the factories of the future will be smarter, safer, and more sustainable—and they will power the next generation of electric mobility.