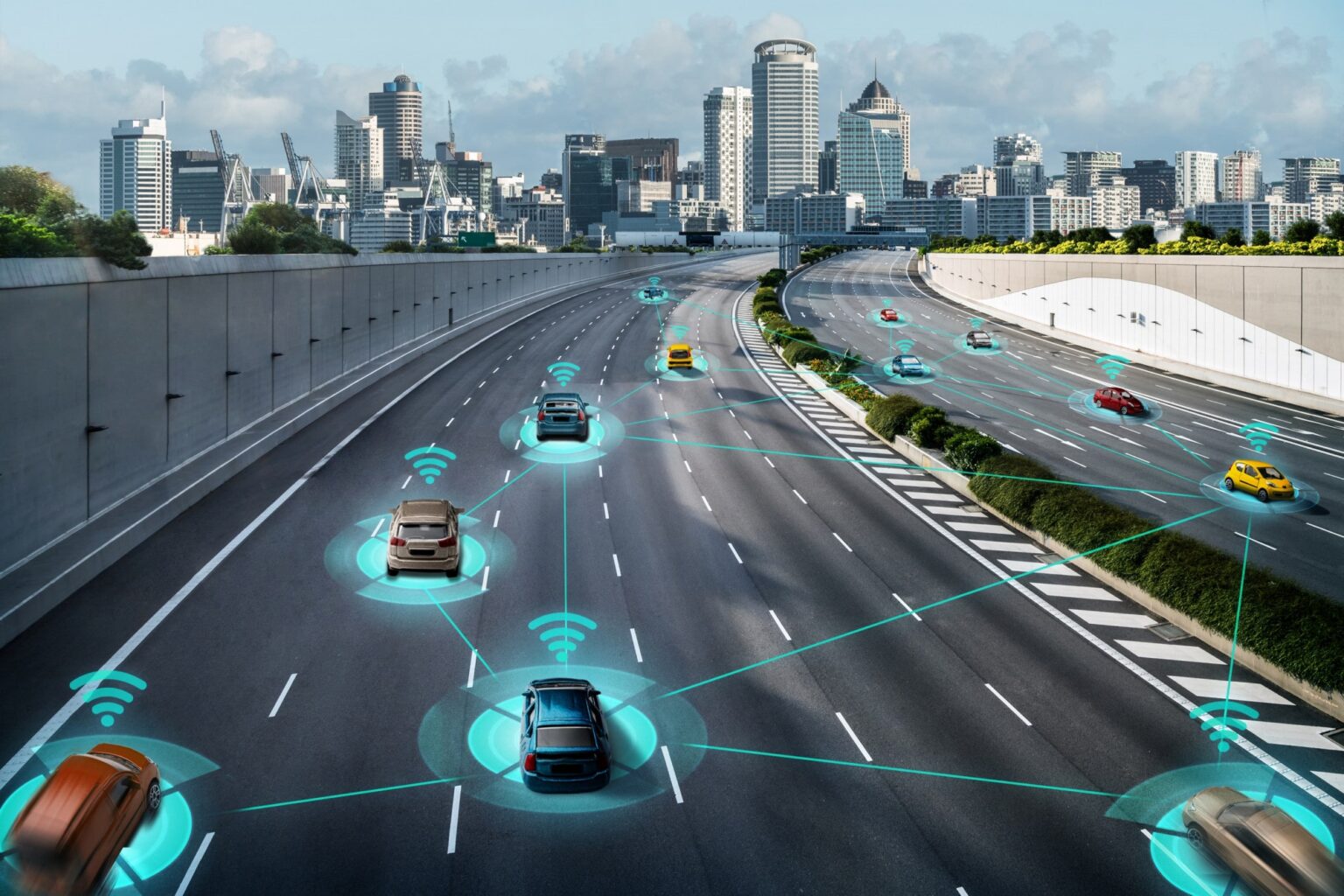
Connected cars represent the convergence of automotive technology and connectivity, revolutionizing the driving experience and transforming mobility. These vehicles are equipped with advanced communication systems and internet connectivity, enabling them to interact with other vehicles, infrastructure, and various digital platforms. Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of connected cars:
- Vehicle Connectivity: Connected cars utilize cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) to connect to the internet. This connectivity allows vehicles to access a wide range of services and information, including real-time traffic updates, weather conditions, streaming media, and software updates.
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication: Connected cars can communicate with other vehicles in their vicinity through V2V communication. This enables the exchange of data related to speed, location, and intentions, facilitating enhanced safety features like collision warnings, adaptive cruise control, and cooperative maneuvering.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Communication: V2I communication enables connected cars to interact with infrastructure elements such as traffic lights, parking systems, and toll booths. This connectivity provides information about traffic conditions, optimal routes, and parking availability, leading to improved efficiency and convenience for drivers.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Connected cars incorporate advanced safety systems that leverage connectivity and real-time data. Examples include lane departure warning, blind-spot monitoring, forward collision warning, and automatic emergency braking. These features enhance driver awareness, mitigate risks, and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
- Advanced Telematics: Connected cars integrate telematics systems that gather and transmit data related to vehicle diagnostics, performance, and usage. This information allows for remote monitoring, proactive maintenance alerts, and predictive analytics, optimizing vehicle performance and reducing downtime.
- Infotainment and Personalization: Connected cars offer advanced infotainment systems that provide a range of features and services. These include navigation with real-time updates, media streaming, voice assistants, smartphone integration, and personalized user profiles. Connectivity enables seamless integration with digital platforms, enhancing the overall driving experience.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Connected cars can receive software updates wirelessly, allowing for continuous improvements and feature enhancements. Over-the-air updates enable bug fixes, security patches, and the addition of new functionalities, ensuring that vehicles stay up-to-date and benefit from the latest advancements.
- Data Analytics and Mobility Services: The vast amount of data generated by connected cars can be analyzed to derive valuable insights. Automotive manufacturers and service providers can leverage this data to optimize fleet management, develop new mobility services, and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency, sustainability, and customer experiences.
Connected cars offer numerous benefits, including improved safety, enhanced convenience, personalized experiences, and optimized performance. However, they also raise concerns regarding data privacy, cybersecurity, and the need for robust communication infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of connected cars with emerging trends such as autonomous driving and smart city initiatives holds great potential for transforming the way we move and interact with transportation systems.