The Year EV Batteries Change Forever
By 2026, electric vehicles will enter their most transformative phase yet. After a decade of rapid adoption, the global EV industry is now racing toward a new benchmark—ultra-safe, fire-proof battery architectures. With safety becoming just as important as range and charging speed, manufacturers are reinventing battery chemistry, pack layout, cooling systems, and AI-driven predictive diagnostics.
2026 is shaping up to be the year when EV batteries stop being “just energy storage” and become smart, self-protecting power systems.
1. Why 2026 Is the Turning Point
The EV industry is reacting to three major pressures:
✓ Rising global safety regulations
Countries in the EU, UAE, India, and the U.S. have introduced stricter rules for thermal runaway prevention and battery recycling.
✓ Consumer demand for safer EVs
Drivers want batteries that are:
-
Non-flammable
-
Longer-lasting
-
Temperature-stable in hot climates
-
Faster to charge without risk
✓ Technology finally catching up
Breakthroughs in solid-state chemistry, silicon anodes, ceramic separators, and BMS (Battery Management System) AI have matured enough for commercial rollout in 2026.
2. Inside the Next-Gen Battery Architectures
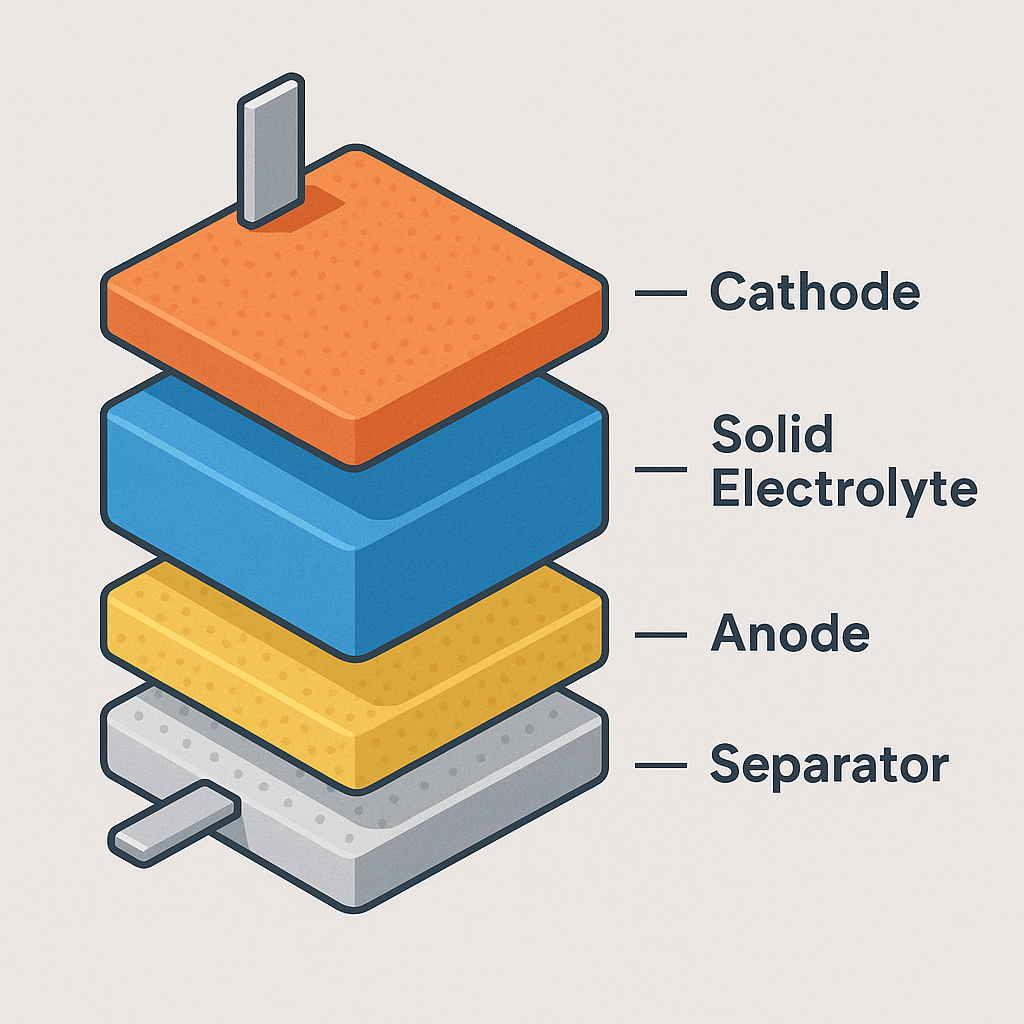
A. Solid-State Batteries (SSB): The Star of 2026
2026 is widely expected to see the first mass-market EVs with full solid-state packs.
Key advantages:
-
Zero liquid electrolyte → No fire risk
-
Higher energy density → 1000+ km range
-
Faster charging → 10–15 minutes
-
Longer life → 5000+ cycles
Toyota, Hyundai, and QuantumScape have already confirmed 2025–2026 pilot launches.
B. LFP 2.0 (Lithium-Iron-Phosphate Reinvented)
LFP batteries, already known for safety, now come with:
-
Manganese-boosted chemistry for more range
-
Nano-crystal cathodes for extreme heat resistance
-
Improved cold-weather performance
These will dominate taxi fleets, delivery EVs, and budget cars worldwide.
C. Cell-to-Pack (CTP) & Cell-to-Chassis (CTC) Structures
Battery giants like CATL and BYD are leading architecture-level innovation:
CTP 3.0 (2026):
-
Packs with no modules, reducing weight
-
15–20% better cooling
-
Lower production costs
CTC Integration:
-
Battery becomes part of the car’s structural frame
-
Higher rigidity → better crash safety
-
Up to 10% more interior space
3. The Rise of AI-Driven Battery Safety
2026 EVs will have predictive intelligence inside every battery pack.
AI-enabled sensors monitor:
-
Temperature spikes (thermal runaway prediction)
-
Internal gas formation
-
Cell pressure changes
-
Micro-cracks in separators
-
Charging patterns and degradation
Benefits:
-
Prevents overheating before it happens
-
Adjusts fast-charging currents dynamically
-
Extends battery life by up to 30%
-
Sends warnings to manufacturers for fleet safety
The EV battery becomes a self-diagnosing, self-healing system.
4. Fire-Proof Cooling Systems Redefined
2026 cooling systems will be triple-layered:
1) Immersion Cooling
Battery cells are immersed in dielectric fluid—cannot catch fire.
2) Vapor-Chamber Cooling (Laptop Tech for EVs)
Super-thin metal plates disperse heat instantly.
3) Graphene Heat Pipes
Graphene-infused channels transfer heat 5x faster than copper.
Combined, they cut fire risk by 90–95%.
5. Global Market Impact: Who Wins the 2026 Race?
Leading automakers gearing for ultra-safe batteries
-
Toyota – solid-state leadership
-
BYD – LFP + blade architecture
-
Tesla – structural battery packs + 4680 optimization
-
Hyundai & Kia – silicon-rich anodes
-
BMW & Mercedes – ceramic solid-state prototypes
Battery giants shaping the future
-
CATL – Qilin & condensed-state technology
-
LG Energy Solution – safety-focused chemistry
-
Panasonic – thermal isolation innovation
6. What Consumers Can Expect in 2026 EV Models
✓ 100% safer batteries with near-zero fire risk
✓ 700–1000 km real-world range
✓ 10–15 min ultrafast charging
✓ Better performance in desert heat (like UAE, Saudi)
✓ Longer warranties (up to 1 million km)
✓ Lower insurance premiums for safer battery tech
2026 won’t just be an upgrade—it will redefine trust in electric mobility.
Conclusion: The Future of EVs Is Ultra-Safe
The race for ultra-safe battery architectures is not just a technological competition—it’s a global movement toward reliable, long-lasting, fire-proof electric mobility.